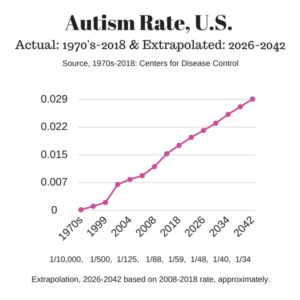
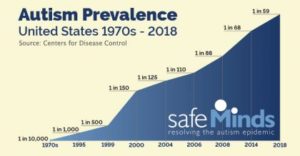
Autism is more of a risk for boys than girls by a factor of four boys for every one girl or three boys for every one girl diagnosed with autism depending on the type of study and diagnostic criteria. There is some speculation that autism in girls presents with less obvious symptoms than in boys. Girls with autism may have less repetitive behavior and be able to fit in socially better than boys with autism and may have less obvious focus on one main topic of interest. (1)
At the other end of the age spectrum females have a greater rate of Alzheimer’s Disease than males. (13)
The difference has been shown to be significant, not just a difference in diagnostic criteria. Estrogen is a female hormone that may be protecting girls from the risk of developing autism but then in menopause is no longer protecting older females from the risk of developing Alzheimer’s Disease. Patients with Autism and Alzheimer’s have been shown to have a tendency to have increased amounts of protein clusters (amyloid beta) in the brain which in normal health would be cleared away. An animal based study found a genetic strain of mice with a clear gender and age difference. Young male mice developed autism like symptoms and older female mice developed Alzheimer’s like symptoms.
A different study found a gender difference in the amount of a protective protein (ADNP) in young male mice with autism like symptoms and older female mice with Alzheimer’s like symptoms. (6) Complete lack of the protective protein leads to very early death with neural tube defects in animal studies. (7) The neuroprotective protein (ADNP) seems to promote autophagy (our body’s recycling method, it makes us more energy efficient and helps detoxify/remove old cells or material such as the beta-amyloid protein for reuse, read more: 14) and the deficit of it may also be involved in schizophrenia. (8) The protein is involved with control of the dendritic branching of brain cells which is typically found to be different in children with autism. The protein also plays a role in regulating over 400 genes involved in embryo development including ApoE and the tau protein which is found to collect in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s Disease in addition to beta-amyloid protein. (9)
The role of apoE involves membranes, cholesterol, cannabinoid receptors and lipid rafts – chemistry geeks have fun, three dimensional drawings and a discussion of cholesterol within the brain and its role in several neurodegenerative diseases is available online in full text, the brain includes 25% of the body’s cholesterol even though the brain only accounts for 2% of the total body weight, on average. (10). A briefer description of the role apoE plays in the brain and with estrogen and Alzheimer’s risk is available with a discussion of the gene differences that are known to increase but not guarantee risk of developing Alzheimer’s Disease. (11)
Disclosure: a genetic screening suggests I do have one of the higher risk differences in the ApoE gene. (rs2254958)
Strategies to help increase autophagy may help reverse some of the risk factors associated with reduced ApoE/reduced ADNP levels –
- vigorous exercise,
- a ketosis promoting, low carbohydrate diet, regularly or occasionally,
- fasting for a day or a partial day occasionally. (14)
The activity of the apoE protein on other genes can be affected by cannabinoids, too little cannabinoids may be a problem or too much.
The take home point – magnesium and adequate cannabinoids seem to be involved in helping clear the protein clusters during normal health.
- Nutritional strategies recommended to help prevent Alzheimer’s disease include increasing intake of magnesium. Research has found that low levels of magnesium promoted build up of beta amyloid protein while high levels of magnesium promoted breakdown of the misshapen proteins.
“Lab studies show that magnesium modulates enzymes involved in amyloid beta production; at low levels, magnesium favors amyloid beta buildup, while at higher levels it favors amyloid beta breakdown.101,102″ [2] (from a 2014 post)
Certain genetic conditions and chronic health conditions or older age can make the body less able to make cannabinoids endogenously/internally. External sources of cannabinoids have been shown to be helpful for clearing the protein clusters involved in Alzheimer’s Disease. (https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/06/160629095609.htm)
An underlying infection with bacteria or yeast may be involved in the buildup of the protein clusters as they have a protective effect against some types of infection, so addressing low grade chronic infection may be needed to help stop the over production of the amyloid beta protein clusters in addition to providing adequate magnesium and cannabinoids. Note that there are non-euphoric cannabinoids and legal food sources in addition to medical marijuana. Pumpkin seeds are a good source, $200 billion per year is estimated to be spent on Alzheimer’s care annually at our current rate of the disease prevalence – that would buy a lot of pumpkin seeds. (15 )
That article also mentions that 192 pharmaceutical chemicals have been anticipated and tested in hope of a cure or effective treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease but which have ultimately not been found to be successful. One hundred and ninety two chemicals tested, one hundred and ninety two chemicals found ineffective – magnesium and cannabinoids however have been found effective at helping the body to naturally break down the tau and beta-amyloid protein clumps that lead to brain damage and later symptoms of dementia in Alzheimer’s Disease and a few other neurological conditions including traumatic brain injuries and autism. (15 ) (links re tau/amyloid in autism & Alzheimers) (links re tau/amyloid protein in traumatic brain injury)
Ibuprofen is a pharmaceutical that is no longer covered by a patent and it has been found to be beneficial in protecting against Alzheimer’s Disease (link: 16) and the underlying reason is likely that ibuprofen prevents the break down of cannabinoids (17)(Search term: “ibuprofen prevents break down of cannabinoids”) – but you need cannabinoids first and some people might no longer be able to make them after a certain age or state of health or may never have been able to make them as well due to genetic differences.
So celebrate protecting your brain today by eating pumpkin seeds, cardamom spice, the herb rosemary, chocolate, or leafy green vegetables. – and the brightly colored tiny inner part of a piece of corn that you can see when eating corn on the cob is also a good source.
- The misshapen tau/amyloid-beta proteins have a protective effect against bacteria and the yeast Candida albicans so a chronic lowgrade infection may be an underlying cause of the accumulation of beta amyloid placques. [3] [4] (from a 2014 post)
There are many more legal food sources of cannabinoids or a precursor available, a longer list is included below. The progression of Alzheimer’s Disease can take twenty years before symptoms are obvious, so getting an early start on protecting against the tau/beta-amyloid protein build-up makes sense to me (Disclosure, I have a direct family history of the disease in older relatives and a genetic screening suggests that I am more at risk, so I am biased towards preventing the disease in my own brain or other family members.)
Phospholipids are part of cannabinoids and other phosphorus containing nutrients are important in energy production. The phospholipids and cannabinoids are important for the health and function of skin and other membranes lining cells and organs, and/or if you care more about having a good hair day than whether you might get Alzheimer’s Disease in several decades, then the phospholipids are also important for hair growth: *The phospholipid mixture in this animal-based study was applied on the skin surface for hair loss associated with inflammatory skin dermatitis: (18)
(Additional Discloure: I am also genetically at risk for Male Pattern Baldness which became visibly apparent when my autoimmune disease was more severe, however with my switch to phospholipid rich foods my hair has since grown back and my autoimmune condition is in remission as long as I continue with my new health habits).
Other nutrients including the B vitamins, vitamin E, and zinc are also important for healthy hair growth (read more) but many of the following list would also be good sources of B vitamins, vitamin E, zinc and other trace minerals and essential omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids. Pumpkin seeds are a good vegetarian source of zinc, otherwise the mineral is more commonly available in meats.
- Food Sources of Phospholipids and other phospho-nutrients: Hemp seed kernels and oil; Artemisia turanica/wormwood leaf; amaranth seed; asparagus; avocado fruit or the inner kernel, dried and powdered; beans/legumes; cardamom seeds and powder; carrots; celery stalks and leaves; cocoa beans and cocoa powder, baker’s chocolate, dark chocolate and to a lesser amount milk chocolate and chocolate syrup; coconut; cumin seed/powder; fennel seed, flax seed, pine nuts; sesame seeds, pumpkin seed kernels, squash seeds; butternut squash and pumpkin; gingko leaf; grapefruit and orange juice with the pulp; Jerusalem artichoke (this is a root vegetable rather than a green artichoke); lettuce, spinach and mustard leaves and other leafy green vegetables and herbs; nuts/peanuts, cashews, walnuts; oats; okra seeds; onion root, leek leaves, garlic; parsnip root; pomegranate seeds and pomegranate peel extract;rice, white or brown but the bran is the best source; rosemary; sorghum; sweet potato or yam; buckwheat (a seed botanically that is not wheat and is gluten free); wheat. (G.26)
That topic took a walk around the block and picked some daisies along the way but the important message might be that eating well and exercising regularly may promote healthy hair, a fit body right now while helping maintain healthy brain function into the future. Genetic susceptibility may be involved in the rate of young males with autism and older females with autism and prevention might include more magnesium and phospholipid rich foods in the diet with a diet that is moderate in carbohydrates and regular vigorous exercise to promote autophagy to help promote the natural recycling of tau and beta-amyloid protein that tends to accumulate in the brains of people with autism and Alzheimer’s Disease. Lack of ADNP protein may lead to lack of ApoE or a genetic difference may cause reduced ApoE and the deficiency may lead to a reduced level of autophagy.
Fasting for a day or partial day occasionally or a low carbohydrate diet, even just a diet balance as low as 30% of calories, and vigorous exercise are three natural ways that may help promote autophagy – our body’s natural method for removing and reusing old cellular material. (14) Those strategies might help a woman with Alzheimer’s risk but for an infant or toddler may need to be adapted to simply allowing vigorous, safe play, and a diet that with a greater percentage of healthy fats than average. The list of phosphonutrient rich foods are generally healthy and safe for prenatal diets or other stages of life and would likely promote a fit body and healthy hair for a person of any age and gender – and what is good for the hair is good for other membranes throughout the body and is also good for the brain. The hair is a protein that is a modified form of skin tissue and so is fingernail protein – beauty is more than skin deep.

Disclaimer: Opinions are my own and the information is provided for educational purposes within the guidelines of fair use. While I am a Registered Dietitian this information is not intended to provide individual health guidance. Please see a health professional for individual health care purposes. Thanks.
- Sarah Deweerdt, Estimate of autism’s sex ratio reaches new low, April 27, 2017, spectrumnews.org https://www.spectrumnews.org/news/estimate-autisms-sex-ratio-reaches-new-low/
- Liam Hawkins, Nutritional Strategies and Alzheimers, March 2013 lifeextension.com, http://www.lifeextension.com/magazine/2013/3/Nutritional-Strategies-to-Combat-Alzheimers/Page-02
- Lisa Conrick, What is Causing Beta-Amyloid Production in Alzheimer’s and Autism?, Oct. 23, 2012, ageofautism.com, http://www.ageofautism.com/2012/10/what-is-causing-beta-amyloid-production-in-alzheimers-and-autism.html
- Molnar Mark, Alzheimer’s Disease Emerging Role of Infection, http://miklossy.ch/
- Why women have more Alzheimer’s disease than men: gender and mitochondrial toxicity of amyloid-beta peptide. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20 Suppl 2:S527-33. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20442496
- Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) exhibits striking sexual dichotomy impacting on autistic and Alzheimer’s pathologies. Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Feb 3;5:e501. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25646590
-
Shmuel Mandel, Gideon Rechavi, Illana Gozes, Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP) differentially interacts with chromatin to regulate genes essential for embryogenesis. Developmental Biology, Volume 303, Issue 2, 15 March 2007, Pages 814-824. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012160606013960
-
Shlomo Sragovich, Avia Merenlender‐Wagner, Illana Gozes, ADNP Plays a Key Role in Autophagy: From Autism to Schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioassays, Volume39, Issue 11, November 2017, Pages 1700054 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/bies.201700054
- Gozes Illana, (2015) Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein (ADNP): from autism to Alzheimer’s disease. SpringerPlus. 4. L37. 10.1186/2193-1801-4-S1-L37. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282802744_Activity-dependent_neuroprotective_protein_ADNP_from_autism_to_Alzheimer’s_disease
- M Maccarrone, G Bernardi, A Finazzi Agrò, and D Centonze, Review: Cannabinoid receptor signalling in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential role for membrane fluidity disturbance. British Journal of
Pharmacology, Themed Issue: Cannabinoids in Biology and Medicine, Part I, Nov. 16, 2010. http://files.iowamedicalmarijuana.org/petition/2012/bjp-aug-2011-1379-1390.pdf - Hilary Lampers, ND, 5 Reasons to Know Your APOE: Understanding Your Alzheimer’s Disease Risk. June 13, 2016 thenatpath.com
- http://thenatpath.com/body/5-reasons-to-know-your-apoe/
-
Maxwell A. Ruby, Daniel K. Nomura, Carolyn S. S. Hudak, Lara M. Mangravite, Sally Chiu, John E. Casida, and Ronald M. Krauss, Overactive endocannabinoid signaling impairs apolipoprotein E-mediated clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 23; 105(38): 14561–14566. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2567196/
- Nick English, Autophagy: The Science-Backed Way to Cleanse Your Body, July 4, 2016, greatist.com, https://greatist.com/live/autophagy-fasting-exercise
- Stuart W Titus, PhD, Dr. Titus’ Insights: Alzheimer’s Research and the Work of Dr. Schubert, Aug. 5, 2016, medicalmarijuanainc.com, https://www.medicalmarijuanainc.com/dr-titus-insights-alzheimers-research-work-dr-schubert/
-
Neuroscientists say daily ibuprofen can prevent Alzheimer’s disease., March 26, 2018, sciencedaily.com, https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/03/180326140239.htm
- K. D. Rainsford, Ibuprofen: Discovery, Development and Therapeutics.
John Wiley & Sons, June 25, 2015, page 134, https://books.google.com/books?id=CAcLCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA134&lpg=PA134&dq=ibuprofen+prevents+break+down+of+cannabinoids&source=bl&ots=oJ_cjSrWXr&sig=yQgwSrdZOkA1MNDkbf7EF7waItY&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjf7ZKPrcnaAhVlneAKHeDyAuAQ6AEIlQEwCA#v=onepage&q=ibuprofen%20prevents%20break%20down%20of%20cannabinoids&f=false - Seong-Hyun Choi, Jeong-Su Moon, Byung-Suk Jeon, Yeon-Jeong Jeon, Byung-Il Yoon, and Chang-Jin Lim, Hair Growth Promoting Potential of Phospholipids Purified from Porcine Lung Tissues. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015 Mar; 23(2): 174–179. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4354319/
- ADNP related syndrome FTNW, *lack of ADNP genetically leads to reduced muscle tone and can cause eating problems in children. https://www.rarechromo.org/media/information/Chromosome%2020/ADNP%20related%20syndrome%20FTNW.pdf